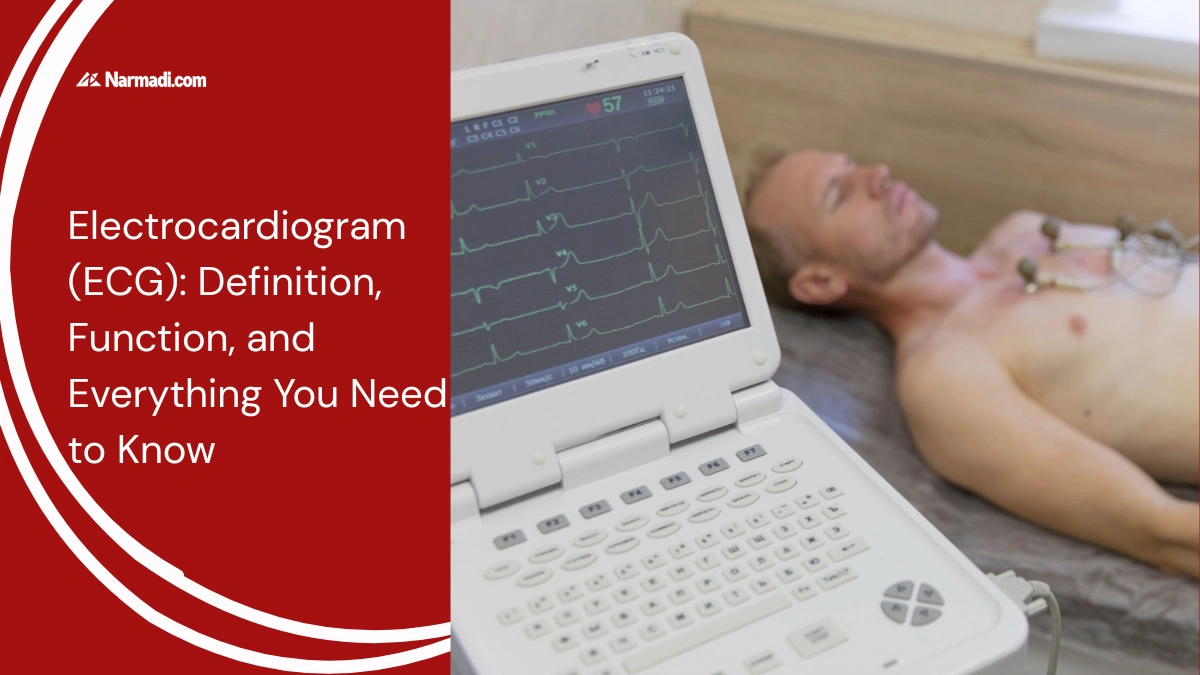
Rapid technological developments have permeated various industrial sectors, and one of the sectors that has benefited most from these developments is the healthcare sector. Technological advancement in the healthcare sector has led to various discoveries, one of which is the electrocardiogram (ECG).
This medical device is used to test the electrical activity of the heart. Electrocardiograms have many functions, ranging from screening for heart attacks, heart muscle disorders (cardiomyopathy), heart rhythm disorders, and coronary heart disease.
When using an electrocardiogram, it is crucial to understand when and how to utilize it effectively. Additionally, you should be aware that there are regulations governing its use in conjunction with WiFi technology.
What is an Electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a medical device used to record the heart’s electrical activity.
The device operates by attaching small electrodes to the skin’s surface.
An ECG helps doctors visualize how electricity flows through the heart during heart muscle contractions and relaxation. From this, they can see whether the heart is functioning normally or if there is a problem.
Its use is crucial for detecting various heart problems, such as irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), insufficient blood flow to the heart (ischemia), heart attack, electrolyte imbalances, or side effects from certain medications. In fact, an EKG is also frequently used for routine heart condition checks or when there are suspicious symptoms.
The Functions
In general, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to assess the heart’s function and detect abnormalities in the organ. Here are some of its functions:
- Assessing risk and readiness: Evaluating the risk of heart disease in individuals with specific risk factors and the patient’s existing heart condition before undergoing other medical procedures.
- Detecting various heart diseases: From cardiomyopathy or heart muscle disorders, arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat, heart attack, and coronary heart disease.
- Investigating symptoms: It can be used to identify the causes of symptoms related to the heart, such as chest pain, headaches, shortness of breath, unusual fatigue, and a heartbeat that feels too fast or too slow.
- Monitoring patient condition: Used to monitor the patient’s heart rate periodically, assess the effectiveness of the treatment given, and check whether the pacemaker implanted is functioning properly.
When is an Electrocardiogram Necessary?
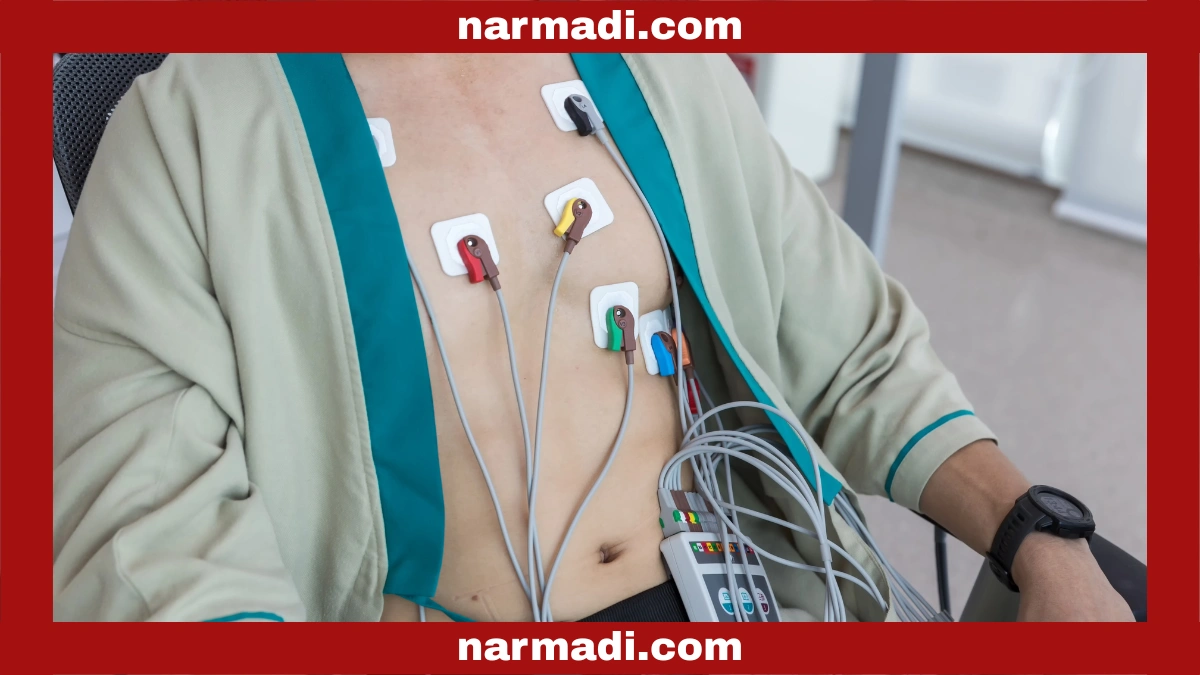

An electrocardiogram is necessary to check the health of a patient’s heart before and after surgery, as well as to assess the effectiveness of heart disease treatment, such as the use of pacemakers and medications.
The following conditions require EKG screening:
- Heart attack
- Heart muscle disorder (cardiomyopathy)
- Heart rhythm disorders
- Coronary heart disease
- Electrolyte disorders
- Drug poisoning
How is an Electrocardiogram Performed?
An electrocardiogram can be performed at a clinic or hospital and takes no more than 10 minutes. Here is a series of procedures for using an ECG:
- The patient will be asked to wear a medical gown.
- The patient must remove all jewelry or other objects from their body.
- The patient will be asked to lie down on a bed.
- Twelve electrodes connected to the ECG machine will be attached to the chest, arms, and legs.
- The ECG machine will record the patient’s heart electrical activity and display it as an electrical waveform graph on the monitor.
- The doctor will then analyze the graph.
- During the ECG examination, the patient will be asked to remain still and refrain from speak, as movement or talking may affect the test results.
During the ECG examination, the patient will be asked to refrain from talking and moving, as this may affect the test results.
The Regulations

An electrocardiogram uses WiFi technology, which operates within a specific frequency spectrum. In every country, all wireless devices are required to have Radio Frequency (RF) Certification.
Electrocardiogram regulations require all radio-frequency-based devices to meet specific technical standards before they can be sold in that country. This certification ensures that products comply with government safety and quality regulations and do not interfere with other communication devices.
Some types of type certification regulations in Asia:
- Indonesia: DJID Certification
- Malaysia: SIRIM Certification
- Thailand: NBTC Certification
- Singapore: IMDA Certification
- Philippines: NTC Certification
- Vietnam: MoST Certification
- Cambodia: TRC Certification
- India: WPC ETA and TEC MTCTE Certification
The certification process involves technical testing, including frequency adjustment, safety checks, and verification of compatibility with the surrounding environment. Once testing is complete, products that pass will be listed in a test report, confirming that they are safe and ready for sale. This report guarantees customers that the product meets technical standards and is secure.
For companies wishing to sell an electrocardiogram, our product compliance services are available to assist with this process. This service includes preparing technical and legal documents, conducting the necessary testing, ensuring regulatory compliance, helping companies streamline the certification process, and providing consumers with confidence in certified products. [UN]