A Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) is an extension of a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). While WLAN is used for local networks, this wireless network is used for networks covering very large areas.
WWAN is very useful in various sectors, such as offices, education, and business. It is used for easy internet access and information exchange. Our lives are inseparable from this network, but are you familiar enough with it?
Don’t worry, this article will help you understand more about WWAN by providing information ranging from its definition, how it works, its components, and its functions. You will even learn how this network differs from WiFi.
What is WWAN?
A Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) is a type of wireless network that covers a wide geographical area, such as a city, country, or even globally. Technologies such as 3G, 4G, and 5G support these wide networks to provide cellular services to users in various locations.
This allows users to connect to the internet and exchange data from almost anywhere without physical cables, as long as there is cellular network coverage.
One example of this wireless network application that we can immediately experience is the cellular service used on smartphones. You can connect to the internet, make calls, or send text messages in various locations from your phone.
Another example of its use is in industry to provide reliable connectivity in locations without cable connections, such as stores, branch offices, and vehicles. In addition, WWAN is also widely used in Internet of Things (IoT) devices to enable them to connect to each other.
Main components
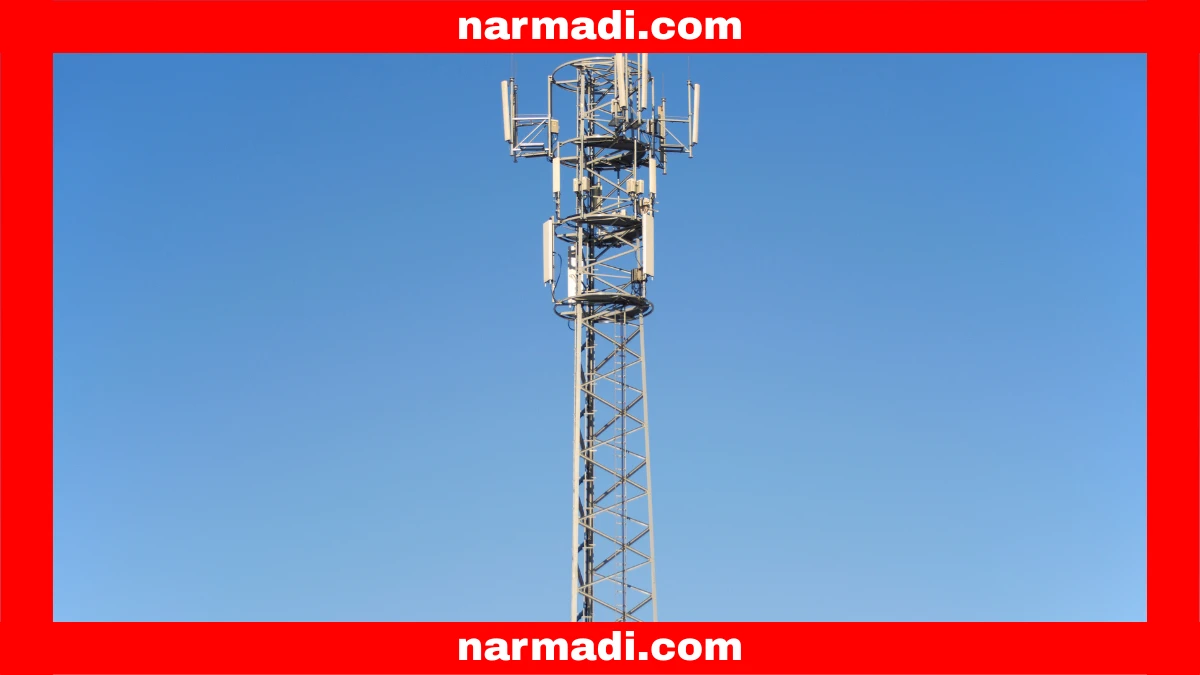

Behind the WWAN network are components that support its operation to deliver maximum performance. These components are modems/routers, SIM cards, cellular networks, and cloud management tools.
- Modems/routers: Devices that connect computing devices to wireless networks, enabling them to send and receive data over the network.
- SIM card: A device that identifies, authenticates, and stores device information on the network.
- Cellular network: This infrastructure includes cell towers, base stations, and other equipment responsible for managing data flow between devices and wireless networks.
- Cloud management tools: A system that facilitates flexible network management/configuration from any location.
How it Works?

By understanding the components behind WWAN, you will be able to more easily understand how it works. Here’s how this wide area network works:
- Cell towers transmit signals: One of the wireless network infrastructures transmits signals to user devices.
- Data routing: After transmitting signals, data is routed through a larger network to its destination.
- Routers process signals: Cellular routers on the network process and send data packets via the shortest available route.
- Connection to cell towers: Modems in devices communicate with nearby cell towers via radio signals through SIM cards connected to service provider networks.
- Internet access: Users can then access the internet via their mobile devices.
Once connected to the internet, mobile devices can transfer data and voice. This process can be done seamlessly between the device and the internet, even when in a geographically large area.
Network and Functions
Internet and data access
With a WWAN network, you can connect to the network and access the internet and data. You can do this without having to connect directly with a cable. This means you can connect to the internet from any location, as long as you are within range of a cellular network.
Long-distance connectivity
Another function of WWAN is to provide long-distance connectivity. This network is capable of connecting devices or networks across a very wide area. Cities, provinces, or even countries can be connected to the network without using cables.
Providing mobility
WWAN is not limited by cables, which is what makes it highly mobile. This network gives users the freedom to move around while staying connected to the internet without cables. This is useful for those who need to access the internet remotely or while traveling.
Flexibility for various devices
Flexibility for various devices is another advantage of WWAN. As we often know, this network is used to connect cell phones or laptops to the network. However, its function can also be used to connect various other devices such as autonomous vehicles, robots, and irrigation systems.
WWAN vs WLAN: What’s the difference?
Here is a brief overview of the differences between WWAN and WLAN.
| Feature | WWAN | WLAN |
| Range | Wide area (cities, countries, global) | Short range (homes, offices, campuses) |
| Technology | Cellular networks (4G, 5G, etc.) | IEEE 802.11 standards (Wi-Fi) |
| Infrastructure | An extensive network of cell towers | Local routers and access points |
| Best For | Mobile devices, traveling, and remote locations | Stationary devices, local internet access |
| Mobility | High, seamless connectivity while moving | Low, requires being within range of an access point |
| Cost | Can be more expensive, often subscription-based | Generally less expensive for the equipment |
Understanding the difference between WWAN and WLAN is very important to bisa memilih teknologi konektivitas yang tepat sesuai kebutuhan mobilitas, jangkauan, dan tujuan penggunaan.
In addition, for manufacturers and importers of network devices, this understanding is also related to regulations. In every country, devices that use WWAN and WLAN technology must obtain Radio Frequency (RF) certification to be legally marketed.
This is information about WWAN, starting from its meaning, components, how it works, and differences from WLAN technology. Hopefully, this article can provide additional information for you in understanding the WWAN network in general and its differences from WLAN.
In addition, you need to know that every product with a WWAN network that is marketed must undergo testing and RF certification from the authorities in charge of Wireless and Telecommunications Devices in your country. [UN]

