Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is one of the technologies that addresses the evolving data transmission landscape and the growing demand for higher bandwidth.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing innovates by revolutionizing fiber optic communications by enabling the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams over a single fiber optic cable, each carried at a different wavelength of light.
If you are not familiar with Wavelength Division Multiplexing, this article will explore thoroughly from the definition, how it works, types, functions, applications, to regulations for its use in Indonesia.
What is Wavelength Division Multiplexing?
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a transmission method in optical fiber that allows the delivery of two or more wavelengths of light simultaneously through a single fiber.
In other words, this technology is an optical multiplexing technique that aims to increase bandwidth capacity. It works by combining multiple data streams and sending them simultaneously over multiple wavelengths of light in the same fiber.
How it Works?
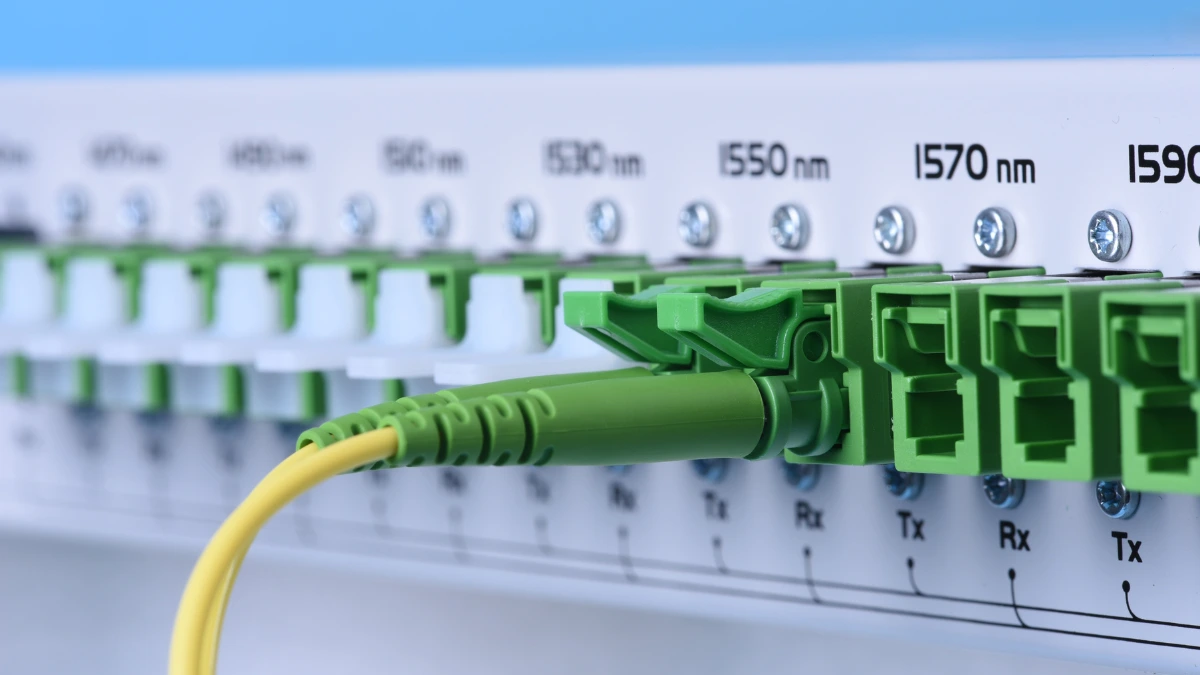
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) devices work by combining light signals of different wavelengths through one optical fiber. Here’s how WDM works in detail:
- Multiplexing: A multiplexer (MUX) device combines multiple light signals of different wavelengths into a single light beam.
- Transmission: This combined light beam is then transmitted through a single optical fiber.
- Signal amplification: During transmission, the signal is subject to attenuation, so an optical amplifier, such as an Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA), is often used to boost the signal.
- Demultiplexing: A demultiplexer (DEMUX) device separates light signals into individual wavelengths.
- Conversion to electrical signals: The separated light signals are then converted into electrical signals by devices such as optical modules, switches, or ONUs/ONTs.
- Signal processing: The electrical signals are then processed and demodulated for further data handling.
The Types
Wavelength Division Multiplex (WDM) is separated in two types that are Dense Wavelength Division Multiplex (DWDM), and Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplex (CWDM).
DWDM itself is a variation of WDM that uses a very tight wavelength spacing that allows more transmission channels.
Meanwhile, CWDM is a variation of WDM that uses a wider wavelength range that is suitable for short-distance transmission.
The Functions of Wavelength Division Multiplexing

The main function of a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) device is to allow multiple light signals of different wavelengths to be sent simultaneously through the same optical fiber. Here are 5 functions of WDM:
1. Increase network capacity
WDM has a function to increase network capacity. It allows more data to be transmitted through a single optical fiber by utilizing various wavelengths of light.
2. Two-way communication
Enabling two-way communication is also one of the functions of WDM. Signals with this tool are able to be sent and received simultaneously on the same optical fiber using different wavelengths.
3. Efficient use of optical fiber
With WDM, the use of existing optical fibers becomes more efficient, so that the need for new optical fiber installations can be reduced. Costs for fiber optic needs also become more efficient.
4. Capacity adjustment
WDM can be adapted to different bandwidth requirements, from CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) to DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing), to support various bandwidth levels.
5. Wide applicability
Another function of WDM is its wide application. It can be used in a variety of applications, including telecommunication networks, data networks, cable networks, and internet networks.
The Applications
Generally, WDM is applied in three fields, namely telecommunication networks, data networks, cable networks, and internet networks. The following is a further explanation regarding the application of WDM:
1. Telecommunication networks
WDM is used for data transmission, internet, video, and other telecommunication services. Furthermore, DWDM technology is capable of transmitting large amounts of data over long distances, such as telecommunication backbone networks that connect cities.
2. Data networks
WDM is used to increase the speed and capacity of data networks. In data center environments that require fast and efficient data transfer, WDM is used to provide high-capacity, low-latency connectivity.
3. Cable networks
The application of WDM in wired networks is very beneficial to increase data transmission capacity and maximize the use of optical fiber, especially for long-distance telecommunication networks and data center interconnections.
4. Internet networks
WDM enables the internet network capacity to be increased by allowing multiple data signals to be sent over a single optical fiber using different wavelengths of light. WDM allows multiple signals to be sent simultaneously without interfering with each other, thus increasing bandwidth and network efficiency.
The Regulations in Indonesia

Wavelength division multiplexing products sold in Indonesia must be certified by the Directorate General of Digital Infrastructure (DJID) under the Ministry of Communication and Digital (KOMDIGI). This is based on KEPMEN No. 6 Tahun 2023, which requires all radio frequency-based devices, including WDM, to meet specific technical standards before being sold in the country.
DJID certification ensures that the product meets government safety and quality regulations and does not interfere with other communication devices. The certification process involves technical testing, such as frequency adjustments, safety checks, and compatibility with the surrounding environment.
Once the tests are completed, products that pass are listed in a Test Result Report, which confirms that the product is safe and ready for sale in Indonesia. This report reassures customers that the product meets technical standards and is secure.
For companies wanting to sell wavelength division multiplex in Indonesia, we are available to assist with this process. This service includes preparing technical and legal documents, conducting required testing, ensuring compliance with regulations, helping companies streamline the certification process, and giving consumers confidence in certified products. [UN]

