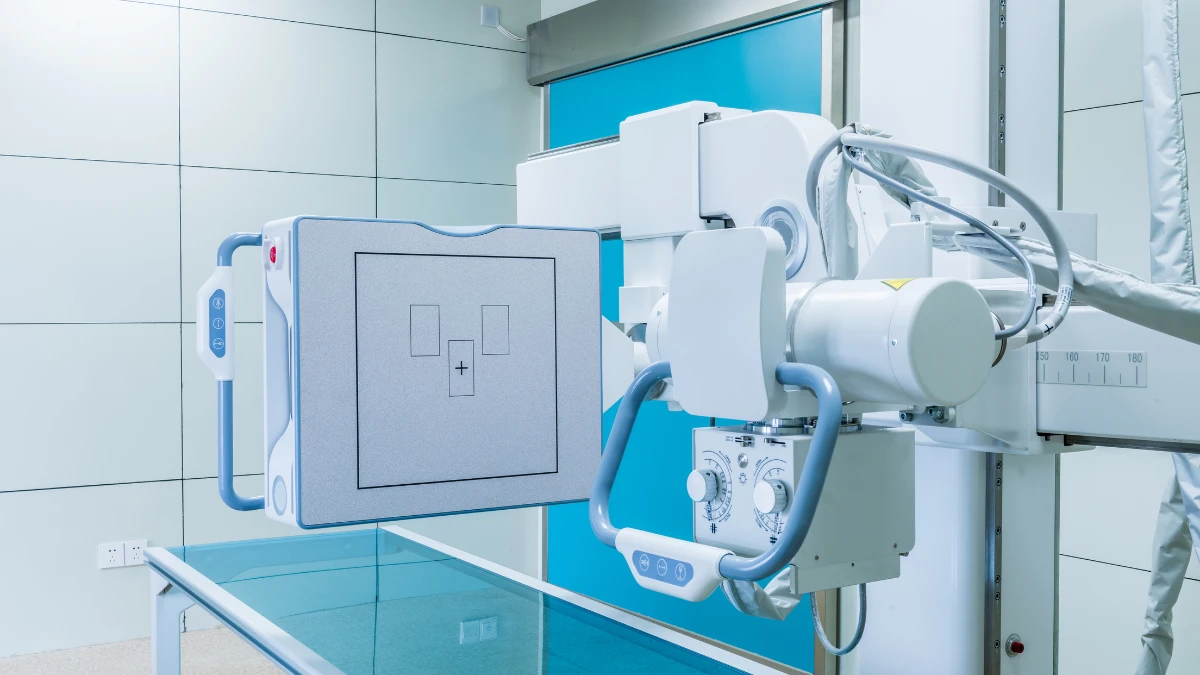
Technology has penetrated various industrial sectors, one of which is health. Digital Radiography (DR) is a medical device with Bluetooth or WiFi technology that has benefits such as flexibility in image processing, reduced medical waste, and wider access, to convenient data storage and sharing.
Are you familiar with the Digital Radiography? This article will review the technology from the definition, how it works, its benefits, and its regulation in Indonesia.
Table of Contents
What is a Digital Radiography?
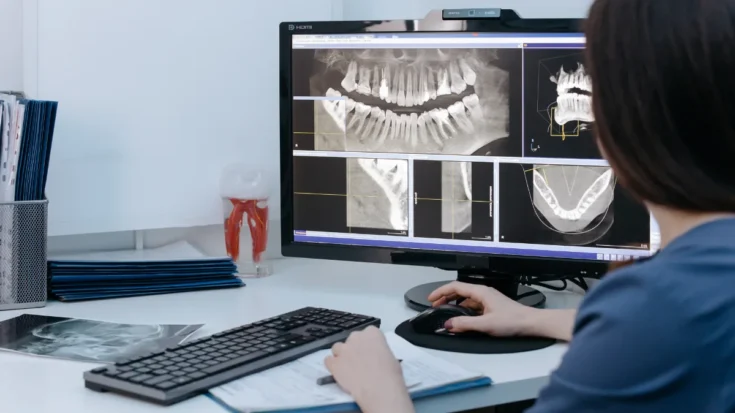
Digital Radiography (DR) is an X-ray-based medical imaging technology that replaces conventional film-based methods with digital sensors.
Also Read
The image processing process that previously used chemicals is now replaced by a computer system directly connected to a monitor or laser printer, allowing instant image display and digital storage.
This system works without the need for manual printing, as the imaging results can be directly displayed and analyzed through digital devices.
The main components in a Digital Radiography system consist of four important parts, namely X-ray Source, Detector, Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), and Computer and Output Device.
How Digital Radiography Works
Digital Radiography (DR) replaces the use of traditional X-ray film with a digital detector. The working process involves the following stages:
- X-ray Exposure: The area of the patient’s body to be examined is irradiated with X-rays.
- Capture of X-rays by the Detector: The X-rays that have penetrated the body are then captured by a digital detector, such as a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) or TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) sensor, according to an explanation from Poly Jaya Medikal.
- Conversion to Digital Format: The detector converts the X-ray radiation into a digital signal.
- Processing Via Computer: This digital signal is processed by a computer system, including image quality enhancement and editing when necessary.
- Image Viewing: The final digital image is displayed directly on the monitor screen for further analysis.
Benefits of Digital Radiography
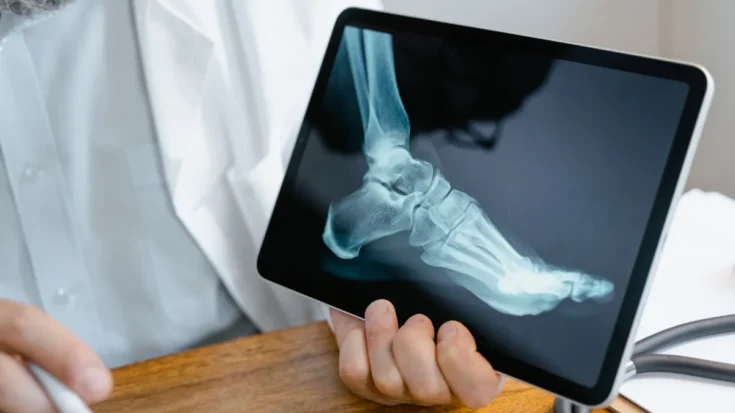
As reported by several sources, here are some of the main benefits of digital radiography:
1. Flexibility in image processing
The resulting images can be digitally enlarged, rotated, or modified, allowing for more detailed analysis according to clinical needs.
2. Reduced medical waste
As it does not require film and chemicals for image processing, digital radiography is more environmentally friendly and reduces the production of medical waste.
3. Wider access
Digital radiography can be performed in facilities ranging from hospitals to small clinics, even in remote locations that have limited access to medical services.
4. Faster image processing
With a digital system, images can be processed instantly, reducing the waiting time for examination results and speeding up medical decision-making by doctors.
5. Lower radiation exposure
Compared to conventional methods, digital radiography generally requires a lower radiation dose due to the higher sensitivity of digital sensors to X-rays.
6. Higher image quality
Digital radiography is capable of producing images with high resolution and wide dynamic range, making it easier to identify small details and improving accuracy in diagnosis.
7. Convenient data storage and sharing
Digital images can be easily stored electronically and shared through networks or other digital devices, supporting inter-health facilities or interprofessional collaboration.
Digital Radiography Regulations in Indonesia

Digital radiography uses communication technologies such as Bluetooth or WiFi that operate within a specific frequency spectrum. In Indonesia, any Bluetooth or WiFi-based wireless device is required to have DJID (Directorate General of Digital Infrastructure) under the Ministry of Communication and Digital (KOMDIGI).
This is based on KEPMEN No. 260 Tahun 2024 and No. 12 Tahun 2025, which require all radio frequency-based devices, including digital radiography, to meet specific technical standards before being sold in the country.
The certification ensures that the product meets government safety and quality regulations and does not interfere with other communication devices. The certification process involves technical testing, such as frequency adjustments, safety checks, and compatibility with the surrounding environment.
Once the tests are completed, products that pass are listed in a Test Result Report, which confirms that the product is safe and ready for sale in Indonesia. This report reassures customers that the product meets technical standards and is secure.
For companies wanting to sell digital radiography in Indonesia, Type Approval Certification Services for ICT Products are available to assist with this process. This service includes preparing technical and legal documents, conducting required testing, ensuring compliance with regulations, helping companies streamline the certification process, and giving consumers confidence in certified products.


















